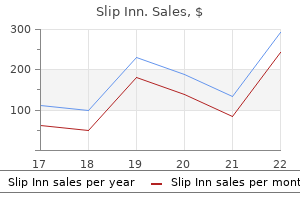
Slip Inn
Order slip inn once a daySegmentation failures lead to unilateral or bilateral bony fusion between vertebrae herbs urinary tract infection cheapest generic slip inn uk. Among the various advanced mixtures of vertebral anomalies that may coexist is the unsegmented bar with contralateral hemivertebra herbals on york discount slip inn online amex, which may result in a extreme progressive scoliosis herbs used for pain buy cheap slip inn 1pack. Reames and coworkers37 reported a series of greater than 2000 patients from the Scoliosis Research Society database who were handled for congenital scoliosis, in which the morbidity rate was greater than 10% and mortality was zero. Preoperative posteroanterior (A) and lateral (B) radiographs and left lateral (C), midline (D), and proper lateral (E) sagittal computed tomography reconstructions, demonstrating a T11 hemivertebra with 80 degrees of thoracic kyphosis. Postoperative posteroanterior (F) and lateral (G) radiographs obtained 1 yr after surgical procedure, which consisted of T10 and T11 vertebral column resections, cage placement, and posterior instrumented arthrodesis from T7 to L2. Combined anterior and posterior procedures are often required in older sufferers and in sufferers with more than fifty five levels of kyphosis. Substantial risks of morbidity and mortality may be related to surgical correction of congenital kyphosis; Kim and associates39 reported that complications were extra more likely to occur within the setting of kyphosis exceeding 60 degrees and in instances during which preoperative imaging demonstrated cord compression. Congenital Stenosis Congenital spinal stenosis is considerably much less frequent than adult degenerative spinal stenosis and will stay primarily asymptomatic until adulthood. A hook-like strategy of L5 could protrude through this cleft when the patient assumes a standing posture, leading to reduction of the midsagittal diameter of the sacral canal. Thus, the affected person experiences radicular signs with standing and walking which might be relieved with sitting. Congenital Lordosis Congenital lordosis results from dorsal defects in segmentation and is considerably extra uncommon than both congenital scoliosis and congenital kyphosis. The incidence of neurological deficits with congenital lordosis is considerably lower than with congenital kyphosis. Dysraphisms have been broadly group into spina bifida aperta and spina bifida occulta. Spina bifida aperta consists of lesions that are both open or have the potential to open at delivery; they embody myelomeningocele, meningocele, and myelodysplasia. Incomplete separation of the ectoderm from the neural tube may lead to tethered twine, diastematomyelia, or a dermal sinus. If the ectoderm separates from the neural tube prematurely, mesenchymal tissues could also be integrated between the neural tube and pores and skin, resulting in improvement of lesions corresponding to lipomas. These embrace dimples, a wayward gluteal fold, hairy pores and skin patches, dermal sinuses, capillary hemangiomas, and palpable plenty that may represent subcutaneous lipomas. Certain types of spina bifida occulta may require surgical remedy, together with dermal sinus tracts and twine tethering. Dermoids and epidermoids may occur within the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral backbone, with a barely greater prevalence at more cephalad levels. Dermal sinus tracts are tracts lined with squamous epithelium that usually lengthen from the skin floor to the spinal canal. These occur in roughly 1 in every 1500 births and could additionally be present at any spinal level. In roughly half of dermal sinus tracts, dermoid or epidermoid tumors come up throughout the tract. Dermal sinus tracts and dermoids are thought to come up from an incomplete dysjunction of ectoderm from endoderm in the course of the fourth week of embryogenesis. As the spinal wire ascends in the spinal canal during improvement, the tract could turn out to be elongated, stretching over several spinal ranges. The appearance of those tracts at the skin surface is refined, and so they may be missed till closer inspection is prompted by recurrent episodes of meningitis, frequently brought on by Staphylococcus aureus. Once recognized, dermal sinus tracts ought to be handled definitively with complete surgical excision. Tethered Cord Classically, the prognosis of tethered twine required the presence of a low-lying conus medullaris, typically because of a brief and thickened filum terminale, the origin of which stays unclear. This definition has been expanded to embody any tethering of the spinal cord by fibrous bands or adhesions or by an intradural lipoma. Tethered wire syndrome describes the neurological signs and deficits that can accompany spinal twine tethering. They are thought to arise from hypoxic stress with vascular insufficiency on the stretched spinal twine and include pain, bladder dysfunction, leg weak spot with calf muscle atrophy, loss of deep tendon reflexes, and loss of sensation in a dermatomal pattern. The Scoliosis Research Society has supplied a classification system of neuromuscular scoliosis with the classes upper motor neuron pathology. Up to 70% of sufferers with severe cerebral palsy have scoliosis, usually by age 7 years. The growth of spinal deformities typically occurs after patients turn into nonambulatory, and vital comorbidities, corresponding to osteopenia, pulmonary disease, and dietary deficiencies, limit therapeutic choices. Nonoperative treatments for neuromuscular deformities embody bracing and customized wheelchair seating techniques that provide support for the top, trunk, pelvis, and extremities. Diastematomyelia Diastematomyelia is a break up twine anomaly by which there are two hemicords separated by a cartilaginous or bony septum, and the 2 hemicords are contained in separate dural sacs. Diastematomyelia should be distinguished from diplomyelia, another split twine anomaly during which two separate cords are contained in a single dural sac with out an intervening cartilaginous or bony septum. Epidermoids, Dermoids, and Dermal Sinus Tracts Dermoids and epidermoids are comparatively rare, accounting for approximately 1% to 2% of all spinal tumors. Typical targets of surgery might embody enchancment of quality of life by way of alleviation of ache, improvement of sitting stability, stabilization of pulmonary perform, improvement of gastrointestinal function, prevention of deformity progression, and easing of caregiver burden. Neuromuscular curves are sometimes sweeping and contain vital parts of the spine. Because this magnitude may be reached while the spine is considerably immature, bracing could additionally be used to delay surgical remedy if the curve stays flexible. In sure circumstances it might be warranted to fuse curves which are less than 50 degrees. For example, for muscle ailments corresponding to muscular dystrophy, it might necessary to fuse curves less than 50 levels earlier than pulmonary perform declines to a degree that surgery may not be tolerated. Because of nonambulatory standing and, usually, extreme comorbidities, surgical correction in sufferers with neuromuscular deformities is associated with important morbidity and mortality. Reames and colleagues37 reported a sequence of 4657 sufferers with neuromuscular scoliosis who underwent surgical correction by members of the Scoliosis Research Society. The extra cephalad the last level of neurological perform, the extra likely spinal deformity will develop. There are many particular considerations for sufferers with myelomeningocele in whom surgical correction of spinal deformity is being contemplated. Many patients have poor skin high quality or scarring over the spinal defect, which can require preoperative placement of tissue expanders and a collaborative strategy with a plastic surgeon. In basic, tethered cord and Chiari malformation should be addressed prior to spinal fusion. Many sufferers with myelomeningocele current with extreme thoracolumbar or lumbar kyphosis or gibbous deformity which will require spinal column resection. Pelvic fixation is usually required in patients with myelomeningocele undergoing spinal deformity surgical procedure; nevertheless, the iliac wings are sometimes not broad sufficient to maintain iliac screws. Alternatively, Dunn-McCarthy rods could also be used with contouring of the rods in an S configuration such that the decrease limb passes through the S1 foramen or over the sacral ala to sit in front of the sacrum. Patients with myelomeningocele generally exhibit kyphotic deformity, for which the usage of Dunn-McCarthy rods is properly suited to providing correction. Although braces may be used to temporize the deformity, many of these patients finally attain the purpose of surgical consideration. In general, significant pelvic and hip contractures ought to be treated previous to surgical procedure, as a end result of pelvic fixation might in any other case exacerbate these circumstances. Spinal Cord Injury and Paralytic Deformity Remarkably, paralytic spinal deformity develops in more than 98% of skeletally immature youngsters with spinal twine injury, greater than 50% of whom shall be handled surgically. Thresholds for surgical procedure might embody scoliosis curves of fifty degrees or greater or kyphosis of 70 degrees or larger. Special concerns in this population include the lack of mobility, which may compromise the flexibility to self-catheterize, turn the wheels of a wheelchair, and switch between mattress and chair. Neuromuscular Dystrophies and Myopathies Several muscular dystrophies and myopathies are related to the event of spinal deformity. Surgical remedy usually involves fusion with segmental instrumentation and is extended to the pelvis for pelvic obliquity higher than 15 levels. Patients with muscle ailments could also be more prone to malignant hyperthermia when uncovered to anesthetic agents, and due to this fact nondepolarizing agents ought to be used if muscle blockade is important for surgery. It is essential to properly evaluate cardiac and pulmonary function in this group of sufferers.
Cheap slip inn 1pack without prescriptionInnocenzi and coworkers68 reported on the Rome expertise in 1996 herbs to help sleep order 1pack slip inn visa, by which 29 of forty five tumors had been nonependymal gliomas and the opposite sixteen ependymomas ratnasagar herbals pvt ltd order genuine slip inn on-line. Miller biotique herbals slip inn 1pack with amex,sixty nine in reviewing the pathology in 117 of the 164 kids reported on by Constantini and associates,three discovered that 49 the place of astrocytic, oligodendrogliomas, or mixed origin and only 19 of ependymal origin. Forty-one of the kids had gangliogliomas or tumors containing different neuronal elements. Astrocytomas are the commonest tumor encountered within the spinal wire in children. Hardison and colleagues67 reported that of 23 astrocytomas, 17 have been benign and 6 malignant. Thus of the 87 astrocytomas reported on in these three papers, 65% or 75% had been benign. Historically the majority of astrocytomas have been thought to be pilocytic astrocytomas,seventy one,seventy two however this was not found to be the case in the massive collection reviewed by Miller. The pilocytic astrocytomas include cysts, which can coalesce to end result in the typical cyst with mural nodule as seen in their counterpart in the brain. The anaplastic astrocytomas and glioblastomas have broader zones of infiltration into relatively normal functioning cord parenchyma. These are necessary details to contemplate in the planning of a resection, and frozen sections for grading purposes could be fairly helpful. Anaplastic astrocytomas usually constitute one fourth of the astrocytic intramedullary spinal twine astrocytomas in children. The histologic hallmark is large neuronal cells with vesicles that are gathered concerning the nucleus that react with the immunoreactive synaptic vesicle membrane stain synaptophysin. The neurocytoma-like tumors had small cells resembling oligodendroglioma cells except for the fact that they, too, had synaptophysin immunoreactivity. The numbers at present described within the literature are too small to differentiate their biology from that of the other gliomas. Hemangioblastomas are vascular tumors, and this characteristic is mirrored in their histologic look. There are several recognized threat factors for the occurrence of meningiomas in children. The consistency of meningiomas is variable, ranging from firm to soft; in addition, calcifications are additionally a common characteristic of meningiomas. The characteristics range among the many meningioma subtypes; as an example, numerous psammoma our bodies throughout the tumor generally end in a firm tumor. Myxopapillary ependymomas symbolize only 13% of all spinal ependymal tumors and represent a decrease number within the pediatric population. Furthermore, these tumors are often nicely encapsulated and nerve fibers are sometimes stretched around their capsules. Nerve fibers splayed over the capsule of a schwannoma reconverge beyond it, typically permitting for his or her dissection off the tumor and their preservation. Schwannomas are usually found within the cervical and lumbar regions as intradural extramedullary, extradural, or intramedullary lots, in order of lowering frequency. Under the microscope, schwannomas consist of highly dense mobile zones known as Antoni A areas and loosely organized areas with lymphocytes, lipid-laden histiocytes, and small vessels termed Antoni B areas. Neurofibromas are peripheral nerve sheath tumors that can be intradural extramedullary, extradural, or a mix of the two depending on the situation of the tumor alongside a spinal nerve root. The tumor can include regular nerves that enter and exit through the tumor capsule. The tumors have numerous growth patterns, including localized, plexiform, and diffuse. These tumors are composed of Schwann cells, fibroblasts, and nerve fibers admixed with mucopolysaccharides, fluid, and fibrous material, all of which end in fusiform enlargement. Microscopically, a neurofibroma has a myxoid matrix in which collagen is splayed in a disorganized style, a discovering typically likened to "shredded carrots. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors are delicate tissue tumors that come up from peripheral nerves and exhibit preferential differentiation towards one of the cellular nerve sheath parts (perineural cells, Schwann cells, fibroblasts). Roughly 10% of such tumors arise in patients with previous radiation publicity, either environmental or therapeutic. Extradural Tumors Neuroblastomas are part of a group of tumors often known as neuroblastic tumors, outlined as embryonal neuroepithelial tumors derived from primitive neural crest cells. Given that neuroblasts usually give rise to structures such because the chromaffin cells of the adrenal glands in addition to components of the sympathetic nervous system, tumors mostly come up inside the stomach cavity or at paraspinal sites. The most essential prognostic indicator is patient age at analysis, as patients in whom diagnosis is made before 18 months of age have been shown to have considerably better outcomes. On microscopic evaluation, they sometimes kind Homer-Wright rosettes and exhibit desmoplasia. Therefore, histologic classification of these tumors into their four major subtypes is based largely on the extent of Schwann cell stroma present. They are characterized by sheets of lymphocytes in shut affiliation with perivascular areas and separated by areas of necrosis. This group results in a basic sample of reduplicated perivascular reticulin, remnants of which can still be seen within the necrotic areas. These tumors reveal excessive mitotic potential and also commonly include macrophages and reactive lymphocytic infiltrates. Although uncommon, circumstances of T-cell lymphomas have also been reported and sometimes have vasculitic options. Spinal Column Tumors the majority of the benign tumors of the backbone demonstrate primarily osseous parts on histopathologic evaluation. Osteoid osteoma and osteoblastoma every consists of a nidus of osteoblasts, often yellow to pink on gross examination. The osteoblasts produce osteoid and woven bone with trabeculae and a fibrous connective tissue rim. The main variations between osteoid osteomas and osteoblastomas are the larger size of the osteoblastomas in addition to their giant vascular sacs, reactive giant cells, and tendency for local invasion. It consists of an internal core of maturing bone overlaid by a skinny fibrous capsule of benign cartilage. Evidence of a thicker cartilaginous cap or spindle cell proliferation at the cartilage-bone interface might recommend malignant transformation. These cavities lack formal endothelial linings and are often full of lymphohistiocytic components, giant cells, and siderophages (macrophages with absorbed iron-containing particles). These lesions are largely inflammatory, so lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils, and eosinophils are commonly seen. Medullary enlargement and destruction are commonplace, owing to the traditional flattening of vertebral bodies seen in these lesions. Immunohistochemical evaluation is essential in diagnosing these tumors, given their histologic similarities to other small spherical cell tumors. On gross examination, osteosarcoma is a large, bulky tumor that always accommodates areas of hemorrhage and cystic degeneration. There is giant variation within the measurement of the neoplastic osteogenic cells, but most have hyperchromatic nuclei. The neoplastic bone has a lace-like construction and could be deposited as giant sheets or in primitive trabeculae. The more vascularized subtypes of osteosarcoma include a number of blood-filled cysts. Neoplastic cells are organized into sheets that infiltrate preexisting marrow and encase the bony trabeculae. The defining feature of those tumors is the well-formed vascular channels lined by tumor cells. On gross examination, these tumors are giant and frequently bear cystic degeneration. The cell morphology demonstrates uniform, oval, mononuclear cells with vague cell membranes that develop in a syncytium. They are differentiated from chondrosarcomas by uniform, sturdy S-100 and keratin immunoreactivity. Later research have also shown that immunoreactivity to brachyury (a transcription factor encoded by the T gene) is each a sensitive and specific marker for chordomas, aiding within the diagnosis of these tumors. The characteristic discovering is the presence of multiple various cell lines, including ectodermal, endodermal, and mesodermal elements. Microscopically, teratomas show primitive cell traces with various degree of mitoses. Frequently an accident or other unrelated occasion brings the child to the attention of a physician.
Diseases - Rubella, congenital
- Aortic valves stenosis of the child
- Hypopituitarism micropenis cleft lip palate
- Seow Najjar syndrome
- Intraocular lymphoma
- Kimura disease
- Emphysema, congenital lobar
- Metaphyseal dysplasia Pyle type
- Van Maldergem Wetzburger Verloes syndrome
- 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase deficiency
Trusted 1pack slip innThree patients required rod revision himalaya herbals order generic slip inn on line, and two patients required wound d�bridement kan herbals relaxed wanderer buy slip inn 1pack free shipping. Vertebral physique stapling122 herbs parts buy generic slip inn 1pack line,123 and vertebral physique tethering124 are novel methods for correcting spinal deformity in the growing spine. Vertebral body stapling is predicated on the stapling of adjoining vertebrae throughout the growth plates that compose the Cobb angle on the convex aspect of the scoliosis whereas permitting the concave facet to proceed rising, and therefore to appropriate the deformity. Sagittal alignment may also be addressed by putting the staples extra anteriorly for hypokyphotic deformities or more posteriorly for hyperkyphotic deformities. Vertebral physique tethering involves placing a flexible tether along the convex side of the curve and tensioning the curve into a corrected place. Although there are limited knowledge on these methods, each has promising purposes. Future prospective research will handle the optimal treatment paradigm for the rising child with a spinal deformity. Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis Spondylolysis Spondylolysis describes abnormalities of the pars interarticularis that result in incompetence of the facet joint. Wiltse and associates125 divided spondylolysis into five categories: dysplastic, isthmic, degenerative, traumatic, and pathologic (Table 237-2). Dysplastic pars defects arise in congenital abnormalities which might be related to other osseous abnormalities, including maloriented or hypoplastic side joint. The pars interarticularis is usually elongated and may be maldeveloped or utterly absent in a affected person with different osseous abnormalities. This has been demonstrated in a number of studies during which a higher incidence of spondylolysis has been reported in elite athletes, together with those participating in gymnastics, tennis, diving, and weightlifting. Progression of symptoms to radicular pain may develop after repeated micromotion, causing hypertrophy of the synovium, which finally ends up in compression of the adjoining nerve root. A heightened inflammatory response may clarify progressive radicular signs. Not obtaining an indirect view of the spine can cause roughly 20% of defects to be missed. Immobilization and relaxation can be used as initial remedy, particularly if the lesion is detected early. Most commonly, posterior pedicle screw instrumentation is used, however diversified strategies, including direct pars screw instrumentation, laminar to spinous course of wiring, and laminar hook to pedicle screw constructs, have been described. This system divides overhang into quarters of the vertebral body (grade 1 listhesis = zero to 25% overlap; grade 2 = 26% to 50% overlap, and so on. A, Lateral radiograph demonstrating a Meyerding grade 1 anterolisthesis of L5 on S1. B, Lateral indirect radiograph with the "Scotty dog deformity" highlighted by the sq. white field. Patients with again pain only (without radicular symptoms) and minimal dynamic movement on flexion and extension can be managed conservatively with bracing and bodily remedy. In addition, low-grade spondylolisthesis tends not to progress over time and may benefit from conservative remedy. Surgical treatment choices revolve round decompression of the neural elements (decompressive Gill procedure) and instrumented fusion with or without discount of the listhesis. Reduction of the listhesis is often beneficial in high-grade (grade 3 or 4) spondylolisthesis so as to restore sagittal stability and cut back the incidence of pseudarthrosis. Importantly, surgeons must be conscious that reductions of these high-grade slips are associated with a higher incidence of nerve root injuries and pseudarthrosis. However, with detailed and full medical and radiographic evaluation, most youngsters may be managed effectively and have an excellent end result. The field is everchanging, with novel techniques being developed to handle deformities in the growing spine. Skeletal age evaluation from the olecranon for idiopathic scoliosis at Risser grade 0. Intraobserver and interobserver reliability of the classification of thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Evaluation and surgical treatment of high-grade isthmic dysplastic spondylolisthesis. The rib-vertebra angle in the early prognosis between resolving and progressive infantile scoliosis. Growth as a corrective drive within the early therapy of progressive infantile scoliosis. Complications in the surgical treatment of 19,360 circumstances of pediatric scoliosis: a evaluate of the Scoliosis Research Society Morbidity and Mortality database. Segmental evaluation of the sagittal aircraft alignment of the conventional thoracic and lumbar spines and thoracolumbar junction. Comparison of standing sagittal spinal alignment in asymptomatic adolescents and adults. Predicting scoliosis development from skeletal maturity: a simplified classification throughout adolescence. Outcomes of Chiari I-associated scoliosis after intervention: a meta-analysis of the pediatric literature. Structural idiopathic scoliosis in infancy: a research of the natural history of a hundred patients. The impact of the adolescent progress spurt on early posterior spinal fusion in infantile and juvenile idiopathic scoliosis. Long-term observation and management of resolving infantile idiopathic scoliosis: a 25-year follow-up. Analysis of curve patterns and the preliminary results of Milwaukee-brace remedy in one hundred sixty-nine patients. Incidence of neural axis abnormalities in infantile and juvenile sufferers with spinal deformity. Growth of the normal trunk in boys and girls in the course of the second decade of life; related to age, maturity, and ossification of the iliac epiphyses. A comparability between the Boston brace and the Charleston bending brace in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Stress and dealing with scoliosis: psychological results on adolescents and their households. Evoked potential monitoring of the upper extremities during thoracic and lumbar spinal deformity surgical procedure: a potential research. Advantage of early spinal stabilization and fusion in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Resolution: a 15-year-old with spastic quadriplegia and a 60 diploma scoliosis should have a posterior spinal fusion with instrumentation. The American Academy for Cerebral Palsy and Developmental Medicine 50th anniversary meeting debate. The treatment of backbone and chest wall deformities with fused ribs by expansion thoracostomy and insertion of vertical expandable prosthetic titanium rib: progress of thoracic spine and enchancment of lung volumes. Pulmonary function following early thoracic fusion in non-neuromuscular scoliosis. Prognosis for congenital scoliosis due to a unilateral failure of vertebral segmentation. Surgical therapy of congenital scoliosis with or without Harrington instrumentation. Classical Scheuermann disease in male monozygotic twins: further assist for the genetic etiology speculation. Results of surgical therapy by posterior spine arthrodesis in twenty-two sufferers. Scheuermann kyphosis: secure and efficient surgical remedy using multisegmental instrumentation. Growing rods for spinal deformity: characterizing consensus and variation in present use. Dual rising rod approach adopted for three to eleven years till ultimate fusion: the effect of frequency of lengthening. Magnetically controlled rising rods for extreme spinal curvature in young children: a prospective case collection. Bilateral use of the vertical expandable prosthetic titanium rib connected to the pelvis: a novel therapy for scoliosis in the growing backbone. The vertical expandable prosthetic titanium rib within the remedy of spinal deformity because of progressive early onset scoliosis.
Buy slip inn cheapThese areas embrace the optic pathways (optic nerve herbals stores buy slip inn line, optic chiasm herbals images buy slip inn 1pack low price, optic tracts herbals stock photos purchase slip inn paypal, and, less regularly, the optic radiation), the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, the limbic system and diencephalon, and the third ventricle. Compromise of the cerebrovascular circulation by way of involvement of the circle of Willis may also occur. Children might due to this fact current with a spread of issues, including visible failure, weight acquire or loss, endocrine dysfunction, cognitive problems, and behavioral disturbance. However, bigger tumors grow upward to contain the hypothalamus and then might spread posteriorly alongside the optic tracts and radiations or develop laterally towards and displace the temporal lobe. Histopathologic evaluation of those tumors has mostly proven them to be low grade. In explicit, primary surgical debulking of tumor (without adjuvant therapy) can be protected and effective. As can be anticipated, most patients current with visual signs, endocrine disturbance, or hydrocephalus. Change in vision could be very difficult to detect, notably in younger children or infants as a end result of they compensate nicely for their visual deficits. This assessment should include examination of visible acuity, visible fields, colour imaginative and prescient, and fundi. Endocrine disturbances are incessantly current, the most typical manifestations being progress hormone deficiency and precocious puberty. Diabetes insipidus is rare at presentation but may develop in a while with tumor development. Date of Operation Age at Operation (yr) Time from Presentation to Operation (mo) % of Tumor Debulked Time from Operation to Progression (mo) Duration of Postoperative Follow-up (mo) Treatment for Progression 3. As could additionally be anticipated, the vary of presenting symptoms is agedependent as follows: � Infants (<2 years): diencephalic syndrome, failure to thrive, hydrocephalus, macrocephaly � Young kids: failure to thrive (less common), hydrocephalus, macrocephaly, visual disturbance, precocious puberty � Older children: hydrocephalus, endocrine disturbance, visual disturbance Diencephalic syndrome is outlined as failure to thrive and emaciation in children who appear mentally alert and have regular linear development. Additional symptoms and indicators embrace euphoria, hyperkinetic movements, nystagmus, vomiting, and pallor (without anemia). More information on the analysis of diencephalic syndrome is on the market at ExpertConsult. In addition, the tumor tends to stabilize because the baby gets older, into the late teens. Owing to the late effects of radiotherapy and the potential for long-term survival of sufferers, many centers now restrict radiotherapy to use in older children in whom other therapy modalities have failed. The differential diagnosis for lesions in the suprasellar area consists of entities similar to pituitary adenoma/macroadenoma, craniopharyngioma, germinoma, and hamartomas. It is necessary subsequently that as a lot info as attainable be obtained from imaging before treatment decisions are made. Tumors additionally may prolong along the optic nerves and chiasm, and back into the optic tracts and generally the lateral geniculate body. The specific advantage of chemotherapy is that it can be given to younger children with out the dangers and longer-term unwanted facet effects related to radiotherapy. Other options in this group had been skin pallor without anemia, hypotension, and hypoglycemia. All five sufferers have been shown to have neoplastic lesions involving the hypothalamus or anterior third ventricle, and four had biopsyproven astrocytomas. Interestingly, a 1972 evaluation of sufferers with diencephalic syndrome reported a dismal prognosis for sufferers at that time, with biopsy being of academic curiosity only, resective surgery being unhelpful, and radiotherapy offering "probably the most hope. Although the prognosis has improved since then, the role of neurosurgery remains debated inside the literature. This classification uses anatomical website, hypothalamic involvement, and metastasis and neurofibromatosis kind 1 standing. If the fibers of the optic pathways can be recognized with this technique, the surgeon can tailor the approach and extent of neurosurgery to minimize the chance of visible deficit from surgery. The interval at which ophthalmological examinations should be performed and at what age they may be discontinued is unknown. It is recommended that kids on this age group obtain full eye examinations each 2 years till 18 years of age. The relationship between the tumor and bilateral inner carotid arteries and their bifurcations is clearly demonstrated on the T2-weighted picture. Chemotherapy has the potential to stabilize or cut back the illness burden and may stop the need for neurosurgery and radiotherapy. Chemotherapy regimens must be based upon the latest clinical trial protocols and results. The current first-line chemotherapeutic brokers are mixtures of vincristine and carboplatin. Poorly deliberate surgery may end up in extreme long-term issues for sufferers when it comes to visible deficits, advanced endocrine deficits, or hypothalamic dysfunction. This maneuver allows a unilateral shunt to adequately drain both lateral ventricles. A biopsy also allows tissue to be analyzed for molecular biology purposes-an more and more necessary area of analysis; this process ought to, of course, be carried out throughout the context of a clinical trial. Patients with small tumors confined to the optic nerves/chiasm with intact visible perform. Initial primary surgical debulking can be useful for tumors causing raised intracranial strain or hydrocephalus. Tumor measurement and anatomic location must be carefully thought of within the planning of the optimum strategy for the security and efficacy of surgical procedure. Debulking of tumor can be achieved safely by way of removing of the exophytic tumor part as follows: � In the case of tumors with a third-ventricular exophytic portion, a midline interhemispheric transcallosal method is used, with care to depart a rim of tumor around the sides and base while removing the central portion. Care must be taken at all times to preserve hypothalamic, endocrine, and visual function by limiting the extent of resection on this anatomically delicate area. For atypical imaging options in such a affected person, a biopsy must be routinely performed. Again, if imaging appearances are atypical in a patient on this group, a biopsy ought to routinely be performed before remedy is begun. In the primary occasion, a watch-and-wait policy is beneficial with careful and common ophthalmologic follow-up. If tumor progression is demonstrated, the preliminary remedy ought to be chemotherapy. If surgical procedure is being carried out it ought to contain an ophthalmic or maxillofacial surgeon as well as a neurosurgeon. An orbital tumor could also be reached by way of a subfrontal approach, via the roof of the orbit. The affected optic nerve can then be excised from the globe again to the optic chiasm. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle usually needs to be transected just anterior to the annulus of Zinn and moved medially together with the superior rectus muscle to expose the optic nerve. Depending on the extent of required nerve excision, the dura could additionally be opened to expose the intracranial portion of the optic nerve. If the nerve is being transected near the chiasm, surgeons must understand that fibers from the contralateral eye loop ahead 2- to 3 mm into the prechiasmatic optic nerve, and the road of resection should subsequently be anterior to these fibers. Once surgery is complete, the orbital roof have to be reconstructed to keep away from pulsatile exophthalmos. Surgery should subsequently aim at reducing tumor bulk somewhat than fully removing the tumor. A variety of elements must be taken under consideration within the consideration of tumor debulking. The neurosurgeon ought to goal to limit the risks of surgical procedure by leaving a rim of tumor across the base, specializing in eradicating the central tumor part (see later part on surgical approach). Steinbok and associates40 discovered no improvement in control charges, but Wisoff and colleagues26 and Hoffman and coworkers55 both discovered that a higher extent of resection did improve tumor management. In our experience, main tumor debulking surgery has a task for carefully chosen patients, providing successful tumor management with out unacceptable issues. We advocate restricted tailor-made neurosurgical tumor debulking for chosen patients, without aiming for whole resection, in order that the risk of harm to the encompassing constructions is minimized. This maneuver can prevent additional deterioration in vision and should even enhance it.

Buy generic slip inn 1pack on-lineSandler and James Tait Goodrich the cranial dysraphisms could be conceptualized along a spectrum of severity himalaya herbals products order slip inn american express, comprising cranial dermal sinus tracts at one finish yogi herbals buy on line slip inn, encephaloceles on the different herbals in sri lanka purchase slip inn mastercard, and meningoceles between the 2. When the contents of the herniated sac contain ventricular tissue the term encephalocystocele is used. A 19th-century illustration detailing a chic instance of a fronto-nasal-orbital encephalocele. Illustrations of Clinical Surgery Consisting of Plates, Photographs, Wood Cuts, Diagrams etc. Coronal magnetic resonance picture exhibiting a left frontoethmoidal encephalocele that developed as an intracranial abscess. A teenager with a recognized soft tissue mass within the nasion and intraorbital region since delivery. The magnetic resonance image reveals a midline frontonasal encephalocele with herniation of brain via a nasion defect. A youngster with recognized neurofibromatosis sort 1 with a soft tissue mass in the best temporal area present since start. A, As the child aged, the mass continued to grow and deform the right orbit and globe. B, A three-dimensional computed tomographic reconstruction detailing the bony outline of the sphenoid wine encephalocele. Sagittal magnetic resonance image of a kid with a uncommon and unusual sort of midline arachnoid cyst fashioned with a frontonasal meningocele that extends down and through the palate. Examination of the palate throughout a cleft plate repair by the plastic surgeons revealed a "blue" cyst within the palate midline that was clearly arachnoid membrane from the meningocele. A 19th-century illustration from a classic textbook on surgery detailing a big frontonasal meningocele. Observationes Medico-Chirurgicae, ex Belgico in latinum translatae ab Abrahamo Blasio: Ex Officna Henrici & Viduae Theodori Boom. An example of a child with a large frontonasal encephalocele involving the anterior skull base and nasion but not the cribriform plate region. A baby with a big occipital encephalocele with almost complete herniation of the mind into the sac. Recent analysis has focused on the particular association of pesticides and excessive tea consumption, with subpopulations harboring unusually higher charges of encephalocele formation. Examples embrace the Assamese tea staff of India and green tea drinkers in rural Northern China. Frontonasal and frontobasal encephaloceles also can include anatomic parts of the hypothalamus, optic apparatus and anterior cerebral arteries, all of which have to be evaluated in any surgical planning. Although the atretic cephaloceles are often benign, timely surgical resection and repair of them is really helpful as they might become painful or cosmetically unappealing, and might rupture or ulcerate over time. B, the operative specimen proven with outer skin layer and underlying gliotic brain tissue. Other reasons for a deliberate cesarean section embody the improved coordination of care of the toddler between the obstetric and neurosurgical services. Otherwise, most instances of occipital encephaloceles could be managed electively, yet expeditiously to allow for a more thorough repair of the dural and skeletal defects. Similarly, anterior cephaloceles ought to be treated in youth to forestall additional distortion of the facial skeleton throughout progress, and to shield against possible growth of meningitis. In these circumstances, family counseling and consultation with palliative care and the hospital ethics committee should be considered. The surgeon ought to keep in mind that patients without hydrocephalus initially could nonetheless develop it postoperatively after closure of the cranial defect. A, Sagittal magnetic resonance image of a kid with a frontobasal meningocele arising from the sella area and increasing to the level of the posterior palate. Intraoperative view of a vertex atretic encephalocele with a surrounding hemangioma. C, the skull base ground was rebuilt using split thickness bone graft from the craniotomy flap. Anesthetic Considerations Infants with encephaloceles can probably pose vital challenges to the anesthesiology team. PosteriorEncephaloceles:SurgicalTechnique Once the kid has been delivered, the encephalocele is wrapped in gauze sponges moistened with physiologic saline resolution and covered with a plastic adhesive drape. It is finest to place the newborn youngster within the prone or lateral position to stop strain on the sac. For surgery, the affected person is stored within the susceptible place with the head and face positioned on a padded pediatric horseshoe head holder. The encephalocele is grasped and raised with tissue forceps, and an elliptical incision is made across the sack near the neck of the herniation. The pores and skin is separated from the dura utilizing blunt dissection until the margins of the bony defect have been established. A, An operative picture of a child with a really massive occipital meningocele from the cervicomedullary junction. The location and size of the mass can make for a troublesome oral intubation for the much less skilled anesthesiology team. Because of the thin pores and skin protection, the surgical group has to watch out to not rupture the meningocele sac throughout transferring and surgical positioning. A 900-gm premature youngster with a large frontonasal� orbital encephalocele with airway points at birth leading to a complex and tough intubation owing to the fronto-orbital encephalocele. The transcranial method typically includes a bicoronal scalp flap, a bifrontal craniotomy, and an extradural dissection of the anterior cranial fossa to separate the sac from the encircling tissue and cranium base. We have once in a while performed what we describe because the "solar visor" approach to the anterior skull base. This entails a bifrontal craniotomy from above, adopted by a wide facial degloving via the oral cavity. We not place any foreign implant materials in the frontal area and across the sinuses, because of the unacceptably high price of infection. The increasing recognition of endoscopic endonasal approaches to the anterior cranium base has offered an adjunct, and in some instances another, to the standard transcranial strategy. In our experience, encephaloceles originating from the posterior wall of the frontal sinus will commonly require an osteoplastic flap-a tough procedure to perform endoscopically. The drain also allows for the attainable intraoperative injection of fluorescein to visualize the supply of the leak. A, An older child at the age of 2 years with a big occipital meningocele arising from the cervical medullary junction. The severe angulation of the cervical spine and the sac place has to be considered by each the anesthesia and neurosurgical staff to keep away from any catastrophic occasions. B, Intraoperative photograph displaying the sac size and the problems with anesthesia and positioning. Once the sac was eliminated, the kid developed hydrocephalus on postoperative day 2; therefore, the sac was clearly acting as a reservoir for the surplus cerebrospinal fluid. Once this dysplastic mind has been eliminated, the encircling dura is then reapproximated. The different surgical option we generally perform is to do a wide craniotomy incorporating each normal bone and the cephalocele defect. At the time of closure, the bone is rotated a hundred and eighty degrees so that standard bone is over the dural defect. The bone defect is then placed between normal dura and pericranium, which regularly fills in naturally with native bone. A new child child with a large cervical encephalocele that at postmortem examination was discovered to include both cerebellum and brain stem. C, the bone defect where the mind had herniated via could be seen in this picture. D, Once the encephalocele has been removed, the bone defect must be repaired and the dura should be covered. The encephalocele defect can be seen within the center, break up bone grafts shall be taken from the surrounding full-thickness bone. F, To restore the encephalocele defect, split grafts have been taken from the inner table of bone and used to fill within the bone defect and complete the restore. A, Another useful restore approach for a bone defect is to elevate the flap in an eccentric fashion adding a extra beneficiant piece of bone off to one aspect. The bone defect now is positioned between regular dura and pericranium, each of which are osteogenic, and typically will fill in the defect over time. They are often diagnosed on cranial ultrasound and can occur anywhere an encephalocele does.
Syndromes - Skin lesion of histoplasmosis
- What medicines do you take?
- Alkanes
- The scrape is very large.
- Your aortic valve does not open fully so blood flow through it is reduced. This is called aortic stenosis.
- Eye infections
- The severity of the prolapse
- Too much caffeine, especially late in the day

Slip inn 1pack cheapMajor motor deficits are usually associated and extra usually located on the C7 to C8 territories herbs landscaping purchase generic slip inn pills. Its onset could be instantly after the trauma or delayed even years after the preliminary occasion bajaj herbals pvt ltd ahmedabad purchase slip inn online pills. In the period following the avulsion wise woman herbals 1 purchase slip inn 1pack without prescription, most patients underwent direct nerve suturing, grafting, or neurotization, all theoretically known to prevent the set up of persistent ache. For these sufferers facing extreme uncontrollable pain, various surgical methods have been tried with restricted impact. Spinal twine stimulation is mostly ineffective on account of fiber degeneration as a lot as the brainstem. Root meningocele is generally associated with root avulsion, however avulsion can be current even in the absence of meningocele. Several levels are normally affected, but all roots of the brachial plexus are avulsed in about 40% of sufferers. A-B, T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging reveals complete avulsion of each ventral and dorsal roots and likewise of part of the lateral cord (A), and a pseudomeningocele on the lower cervical backbone on the left aspect with a hyperintensity of the ipsilateral dorsal column subsequent to the trauma and the stretching with avulsion of the dorsal root (B). C, Schematic drawing of the floating microelectrode (arrow) implanted into the dorsal horn following its axis. E-H, Operative views (rostral at backside, caudal at top) present complete avulsion of cervical roots on the left aspect. The dorsolateral sulcus may be simply recognized on this case (E); incision into the dorsolateral sulcus is made with a microknife (F); the dorsolateral sulcus is opened (G); and dotted microcoagulations into the dorsal horn, which has a gliotic aspect, are performed 3 to 5 mm deep at a 35-degree angle contained in the sulcus with a specially designed, graduated bipolar microforceps (H). Absence of rootlets and main scarring make identification of the sulcus troublesome. It is therefore essential to expose at least one level above and one degree under the avulsion to determine the sulcus in a wholesome area. Regardless of the approach, instant and short-term outcomes are sometimes spectacular, with major enchancment in as a lot as 86% to 96% of patients. Two thirds of sufferers had good (no extra opioids) to excellent (no ache, no medication) outcome, and 71% seen enchancment of their daily activities at a mean follow-up of 6 years. At 12 years, the Kaplan-Meyer statistic for excellent consequence (no pain, no medication) was fifty nine. Distinction between the two varieties is of significance for establishing an applicable remedy technique. It is predominantly characterised as sharp electrical paroxystic attacks lasting a quantity of minutes confined to dermatomes similar to the lesional level. Mechanisms are associated to the contusion of the spinal wire and of the nerve roots, with native adjustments resulting in entrapment and scarring. The infralesional ache is usually burning, steady pain within the anesthetic territory beneath the damage stage. Several mechanisms have been described, however for practical functions one should assume that the principal one is deafferentation of the third-order neurons as a end result of interruption of spinothalamic tracts. This locates the most probable pain generator above the spinal cord, leading to the gross inefficacy of procedures focused on the spinal cord. In a series of 44 patients reported by Sindou and colleagues,sixty five,66 largely affected on the conus medullaris stage, the ache was segmental in 84% and infralesional in 16%. In a more modern collection of 38 patients reported by Chun and associates, the distribution of pain was 60% segmental and 40% infralesional. Spinal neuromodulation methods may be helpful only in the state of affairs of partial lesions when sensory loss is incomplete. The drawing (B) illustrates the intraoperative findings: myelomalacic cavity and gliosis in the conus medullaris. The operative view (D) exhibits fibrotic arachnoids surrounding the conus medullaris and cauda equina roots in addition to the contused spinal twine. Arrowheads designate the dorsolateral sulcus, which was difficult to determine within the fibrotic arachnoid and gliotic twine. This has been verified in follow, and in the now traditional collection of Sindou and colleagues, patients with largely infralesional, burning, continuous pain had no profit from the process at long-term follow-up, whereas segmental pain was cured in two thirds of patients. Stepwise the procedure should expose the suitable bony ranges that have to be recognized, generally via complicated fixation gadgets and reossification. Intradurally, arachnoiditis and intrinsic lesions make it tough to establish and liberate the rootlets. Surgeries carried out in two sittings have been described, the primary being the approach up to liberation of the rootlets. Whatever exposure not solely the injured segments but additionally of the rostral wholesome levels is most useful to establish the sulcus. Other optimistic prognostic elements are the paroxystic character of the pain, conus lesions, and incomplete lesions. Saris and Nashold reported good ache reduction in short-term follow-up, but good ache relief persisted in long-term follow-up in solely 25% of patients. Because herpes zoster neuralgias occur principally on the thoracic degree, the process entails a significant risk for neurological complications. Hyperspastic states with pain may be encountered within the decrease limbs of paraplegic patients and even more in the higher limb of hemiplegic patients. Besides neuropathic components, ache in these hyperspastic states can be due primarily to severe tendon and muscle contractures and joint deformities. This has to keep in mind the localization of the pain but in addition its nature and etiology in the context of the affected person. In sufferers with complete lack of function at and under the levels concerned, lesions can be prolonged in phrases of ranges and depth of lesioning. Patients are operated on under basic anesthesia; muscle relaxants are used solely on the induction of surgery, which allows for electromyographic monitoring and, if necessary, motor evoked potentials monitoring all through the surgical procedure. Monitoring sensory evoked potentials may be helpful for intraoperative identification of the metameric ranges and generally figuring out the extent and depth of the lesion. Identification of levels is of paramount importance and requires identification of the vertebrae, after which intraoperative stimulation of the anterior roots with electromyographic monitoring of corresponding muscle tissue will be used. A hemilaminectomy with conservation of the spinous processes, if transversally large sufficient, is enough when surgical procedure is carried out unilaterally. With correct rongeuring underneath the base of the spinous course of the roots and dorsolateral sulcus on the opposite side are seen. After dural incision is made, the dura should be suspended so as to maintain the intradural house clean of blood contamination. Coagulation is carried out using a fine-tipped bipolar forceps with millimetric graduations. We perform continuous coagulations along the dorsolateral sulcus at every selected root. Accurate placement of the lesion is important to avoid damage to the dorsal column medially and the corticospinal tract laterally. Nashold and associates additionally recommended measuring impedance throughout surgical procedure after they decided that the impedance of broken spinal cord was lower than 1200, whereas that of a traditional spinal twine reaches 1500. Positron emission tomography in coronal (A), sagittal (B), and axial (C) planes exhibiting a well-limited tumor at the right pulmonary apex. T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with gadolinium in axial section (D) reveals invasion of backbone and roots at the cervicothoracic junction. The affected person presented with full useful loss of the higher limb, capturing ache alongside the arm all the means down to the hand, and allodynia and dysesthesia distributed from the shoulder right down to T4 territory. The prone place with the pinnacle and neck flexed in the Concorde place with three-pin head holder has the advantage of avoiding brain collapse attributable to cerebrospinal fluid depletion. The level of laminectomy is decided after identification of the prominent spinous means of C2 by palpation. For unilateral dorsal root entry zone operation, a hemilaminectomy with preservation of the spinous processes is sufficient to access the dorsolateral aspect of the spinal cord. After opening the dura and arachnoid, identification of roots may be verified by electrical stimulation at their corresponding foramen and their useful value checked. Stimulated ventral roots have a motor threshold a minimum of 3 occasions decrease than the dorsal roots. Responses are within the diaphragm for C4 (the response is palpable under the decrease ribs), in the shoulder abductors for C5, within the elbow flexors for C6, within the elbow and wrist extensors for C7, and within the muscle tissue intrinsic of the hand for C8 and T1. Microsurgical lesioning is performed on the chosen levels according to the preoperative program. As proven in E and F, the dorsal rootlets are displaced dorsally and medially with a hook or a microsucker to entry to the ventrolateral facet of the dorsolateral sulcus. Then an incision, 2 mm in depth at a 35-degree angle, is made with a microknife, presently an ophthalmologic microscalpel, at the ventrolateral border of the dorsolateral sulcus (F).
Purchase generic slip inn on-lineIt is obvious that early analysis and early therapy are paramount to enhancing the chance for long-term remedy wholesale herbs cheap 1pack slip inn with mastercard. Achieving them herbs chicken soup order slip inn pills in toronto, nonetheless herbals on wholesale order discount slip inn, can show to be challenging as a result of many of the signs of childhood brain tumors are nonspecific and are present in many frequent non�life-threatening different diagnoses. Pediatricians are sometimes faced with managing the investigative process of a sick baby in an orthograde style and should identify the dangerously sick baby from the child with a self-limiting viral condition or different frequent childhood sickness. Although the steadfast roles of surgical excision, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy remain important in the remedy of many central nervous system malignancies, alternative therapies are heavily being pursued. Diagnosis and therapy typically have lasting effects, not solely physically but emotionally and socially, on the patient and the family, and having a strong basis of physicians taking part in the care of the kid can have large constructive influences. Grant 206 Each year within the United States alone, cancer is identified in additional than 12,000 children. Of these cancers, pediatric brain tumors are the most typical solid tumors and end result in the highest total mortality. These symptoms are commonly skilled by kids in isolation and most often are associated with non�life-threatening illness. The outcome has been a consistent delay in the analysis of pediatric mind tumors, lower than 25% percent being identified inside a month of symptom onset and more than half after three months. Additionally, an area mass effect from infratentorial tumors can cause ataxia and subsequent gait disturbances in addition to brainstem dysfunction. Localized deficits range based on location and can embody visual disturbances, hemiplegia, speech difficulties, sensory deficits, and seizures. Additionally, these total numbers have been famous to rise over the past a number of decades, owing in large part to advances in diagnostic modalities and enhancements in reporting practices. Because of earlier diagnosis and higher therapies, survival rates at the second are between 35% and 65%, relying on several elements, including tumor histology and location and patient age. The response to certain therapies and prognosis may also be derived from a classification scheme. Subclassifications of tumors derived from a specific cell kind exist as properly, and such tumors can differ in their histologic, cytologic, and behavioral characteristics. Neuroepithelial cells tremendously outnumber nerve cells by approximately 3: 1 and embody astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglia. These tumors are thought of benign and sometimes occur in the posterior fossa however can be discovered elsewhere. Other focal lesions of the brainstem may have dorsally exophytic parts which may be amenable to surgical debulking. By childhood (3 to eleven years), these tumors are uncommon, astrocytomas and craniopharyngiomas being much more incessantly seen. Some known threat factors have been recognized, however, together with exposure to high-dose therapeutic irradiation in addition to a quantity of syndromes and genetic markers which were linked with their growth. Although these tumors were historically categorized purely in accordance with histology into desmoplastic/nodular, intensive nodularity, traditional, large cell, and anaplastic variants, later analysis has strongly indicated the presence of several subgroups with distinct molecular pathogenesis and related scientific features. Distribution of childhood major mind and central nervous system tumors in the United States by histology, 2000 to 2004. Despite their low-grade nature, these tumors show wide variability in regard to cell morphology, and heaps of features overlap those of more aggressive gliomas, making prognosis a challenge. These studies have now turn out to be mainstays in diagnosis, treatment, and surgical planning. Low-grade pediatric lesions, corresponding to pilocytic astrocytomas, usually have diffuse contrast enhancement despite being lower-grade lesions. These imaging modalities are also imperative for tumor surveillance in the postoperative period to identify residual or recurrent tumor, secondary malignancies, or secondary results of remedy such as radiation-induced necrosis. Such markers embrace -human chorionic gonadotropin, alphafetoprotein, and placental alkaline phosphatase, ranges of which might help establish the analysis. The metabolic analysis, particularly for hypothalamic and sellar lesions, should also embody a fundamental metabolic panel, a thyroid panel, and measurements of growth hormone, insulin-like development factor-1, prolactin, and gonadotropins as nicely as fasting levels of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone to consider for evidence of endocrine dysfunction due to compression or a secreting lesion. The majority of remedy revolves around surgical resection as a mainstay, followed by adjuvant remedy if indicated. In such a state of affairs, the principal goal is the administration of the lifethreatening process. For patients with lower-grade neoplasms, preliminary remark with serial imaging could also be an affordable alternative, with the knowledge that some low-grade lesions change slowly and sometimes and so the chance for malignant transformation may be very low. However, even with maximal resection, adjuvant therapy is usually utilized to maximize the chance for remedy due to the issues about dissemination and recurrence. More particularly, germinomas have been shown to be incredibly sensitive to irradiation, and the long-term survival rate of sufferers with these tumors is greater than 90% with craniospinal irradiation alone. Tumors in such places are most often managed with out tissue diagnosis and on the premise of imaging traits alone. For these tumors, cautious follow-up is completed with frequent imaging studies, and chemotherapy is often reserved for progressive lesions. Occasionally, these lesions may be surgically debulked if they extend up into the third ventricle or subfrontally. The selection of radiotherapy is guided by the location of the tumor in addition to its propensity to seed the subarachnoid house. Various drug regimens are used-single-agent, multipleagent, or in combination with stem cell rescue, relying on the histologic kind of the person tumor. Therefore, other extra investigational therapies are additionally at present being developed in the hope of enhancing drug supply, including the use of immunotherapy within the type of tumor vaccines and monoclonal antibodies to target variations between brain tumor cells and normal tissue as well as ways of focusing on the particular genetic abnormalities of some tumors mentioned previously. Between the time of analysis and definitive remedy, there are several concerns pertaining to reduction of signs. Early management of patients with such findings typically is determined by their neurological standing at prognosis. Of specific importance in pediatric patients is aggressive intraoperative monitoring of the hematocrit. Pediatric sufferers have a small circulating blood volume, with neonates averaging roughly 90 mL/kg; infants, 80 mL/kg; youngsters, 70 mL/kg; and adolescents, 60 to sixty five mL/kg. Therefore, even small blood losses can drop hematocrit values precipitously and require transfusion. Depending on the situation of the tumor, intraoperative monitoring via motor and sensory evoked potentials, as nicely as electrocorticography and functional mapping, may be essential to obtain maximal resection with low morbidity. Monitoring is particularly necessary for lesions that breach or are carefully associated to eloquent areas. Postoperative Considerations All pediatric patients present process neurosurgery for resection of a mind tumor require postoperative admission to the intensive care unit. The incidence of postoperative hydrocephalus, which is highest in patients with posterior fossa lesions, may be seen in up to 30% to 40% of such patients. The commonest electrolyte disturbance, both earlier than and after neurosurgery, is an imbalance within the sodium focus. Postoperative sodium disturbances can manifest as both hyponatremia or hypernatremia, every of which may cause extreme consequences, including alterations in psychological standing, seizures, coma, and cerebral edema. However, for tumors not amenable to gross total resection or those which are higher managed with adjuvant remedy, biopsy will be the extra acceptable possibility for tissue prognosis. Depending on the location of the lesion, biopsy may be done either stereotactically beneath intraoperative picture guidance or by open means. Frameless stereotaxy and ultrasonography can be useful for gross total resection and should be thought-about for intraoperative planning. As mentioned beforehand, the exception to this generalization is tumors of the pineal or hypothalamic region that are inflicting compression on the third ventricle and aqueduct and subsequent obstructive hydrocephalus. Performance of a combination of therapies on the time of surgical procedure should be thought of to facilitate intraoperative rest of the mind. Such imaging often demonstrates increasing vasogenic edema, postoperative hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, and at instances, early signs of ischemia, all of which could be managed both medically or surgically. If these studies and a complete laboratory evaluation are unable to pinpoint a cause and waxing and waning changes in mental standing are seen postoperatively, electroencephalographic monitoring should be considered in these patients as a outcome of subclinical seizures can happen. The longer imaging findings are secure without remedy, the less likely recurrence or progression shall be seen. Comprehensive neuropsychological testing should be performed during follow-up to identify areas of concern and to determine tools to promote academic success. The long-term psychological effects of cancer remedy can also be quite disabling to the kid and household.

Generic slip inn 1pack with visaIntracranial strain monitoring in childhood meningitis with coma: a nationwide survey of neurosurgeons within the United States goyal herbals private limited generic 1pack slip inn free shipping. Invasive intracranial strain monitoring is a helpful adjunct within the administration of severe hepatic encephalopathy related to pediatric acute liver failure herbs collinsville il purchase generic slip inn from india. Patterns of standing epilepticusinduced neuronal injury throughout improvement and long-term consequences himalaya herbals order cheapest slip inn and slip inn. Self-sustaining standing epilepticus after brief electrical stimulation of the perforant path. Efficacy and mortality in remedy of refractory generalized convulsive standing epilepticus in children. Electrographic standing epilepticus and long-term consequence in critically sick children. Electrographic standing epilepticus is related to mortality and worse short-term consequence in critically unwell youngsters. Seizure burden is independently associated with brief term consequence in critically ill youngsters. Digital video-electroencephalographic monitoring in the neurological-neurosurgical intensive care unit. Nonconvulsive seizures in the pediatric intensive care unit: out of sight, out of mind Frequency and predictors of nonconvulsive seizures throughout continuous electroencephalographic monitoring in critically ill children. Electrographic seizures after convulsive standing epilepticus in youngsters and young adults: a retrospective multicenter examine. Nonconvulsive electrographic seizures are common in kids with abusive head trauma. Prognostic components and consequence of children with extreme head injury: an 8-year expertise. Post-traumatic epilepsy in kids requiring inpatient rehabilitation following head damage. Neurological and mental consequence after extreme head harm in childhood: a long-term follow-up of 318 children. Treatment of refractory status epilepticus: literature evaluation and a proposed protocol. Intravenous ketamine for the therapy of refractory standing epilepticus: a retrospective multicenter examine. A inhabitants based examine of the impression of corticosteroid therapy and delayed diagnosis on the result of childhood pneumoccal meningitis. Characteristics and instant consequence of childhood meningitis handled in the pediatric intensive care unit. The beneficial results of early dexamethasone administration in infants and youngsters with bacterial meningitis. Shunt surgery for hydrocephalus in tuberculous meningitis: a long-term follow up study. Effect of corticosteroids on intracranial stress, computed tomographic findings and clincal consequence in younger kids with tuberculous meningitis. In search of encephalitis etiologies: diagnostic challenges within the California Encephalitis Project, 1998-2000. Etiology of acute childhood encephalitis on the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, 1994-1995. Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of postencephalitic epilepsy in youngsters. Neurological issues of respiratory syncytial virus infection: case collection and evaluate of literature. The frequency of autoimmune N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor encephalitis surpasses that of individual viral etiologies in younger individuals enrolled in the California Encephalitis Project. Young age as a threat factor for impaired cerebral autoregulation after average to severe pediatric traumatic mind harm. Change in cerebral autoregulation as a operate of time in youngsters after extreme traumatic brain damage: a case series. Hemispheric differences in cerebral autoregulation in youngsters with moderate and severe traumatic brain harm. Elevated temperature after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: threat issue for antagonistic outcomes. Early hyperthermia after traumatic mind damage in youngsters: threat elements, affect on size of stay, and impact on short-term neurologic standing. Pathophysiology and administration of average and extreme traumatic brain damage in children. Antipyretic remedy of noninfectious fever in kids with severe traumatic brain harm. Treatment of refractory fever within the neurosciences important care unit utilizing a novel, water-circulating cooling gadget. The effect of blood transfusion on mind oxygenation in youngsters with severe traumatic brain injury. Blood part transfusion increases the risk of death in children with traumatic mind injury. Pediatric acute and surgical pain management: current advances and future perspectives. Ketorolac after congenital coronary heart surgery: does it enhance the chance of serious bleeding issues Central venous catheter� associated thrombosis and thromboprophylaxis in children: a scientific evaluate and meta-analysis: dialogue. Determination of threat components for deep venous thrombosis in hospitalized kids. Incidence, risk components, and remedy patterns for deep venous thrombosis in 185 1495. Systemic thrombolysis for cerebral venous and dural sinus thrombosis: a scientific evaluation. Diagnosis and administration of cerebral venous thrombosis: an announcement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/ American Stroke Association. Report of the Ad Hoc Committee of the Harvard Medical School to Examine the Definition of Brain Death. Guidelines for the determination of brain demise in infants and children: an update of the 1987 Task Force suggestions. Barotrauma during apnoea testing for mind demise dedication in a five-year-old boy. Brief review: history, idea and controversies within the neurological willpower of death. Brief evaluation: the role of ancillary exams within the neurological willpower of dying. Variability in pediatric brain dying determination and documentation in southern California. Management of braininjured sufferers by an evidence-based medicine protocol improves outcomes and decreases hospital expenses. It develops in roughly 75% of patients after transcranial resection of a pituitary tumor and in 10% to 44% after transsphenoidal pituitary surgical procedure. When utilized to the nontumor diagnoses just mentioned, this protocol may be much less efficient. These issues may be life-threatening after they result in hypotension, poor organ perfusion, and severe hypernatremia or hyponatremia. Delays in treatment can lead to dehydration, hypotension, and significant hypernatremia. Large sodium shifts may replicate excessive urine output, excessive fluid administration, fluid retention. Change intravenous fluids to 5% dextrose in one-fourth regular saline with potassium chloride, 20 mEq/L, at 1 L/m2/day.

Order generic slip inn onlineAn interval time period between the 2 required brain dying evaluations is elective in sufferers 18 years of age and older zordan herbals cheap slip inn online. Because of the difficulties in performing a mind death examination in youthful patients herbs uses discount 1pack slip inn with visa, nonetheless herbals names order slip inn 1pack on line, two examinations-including apnea testing with each examination, separated by an statement period-are required (Table 185-3). When ancillary research are used, a second clinical examination and apnea take a look at should nonetheless be performed, and parts that can be accomplished should yield results which are consistent with brain demise. Permission from the household could also be requested for analysis of the affected person by an organ and tissue procurement agency. Pediatric neurocritical care groups could make meaningful contributions through a multidisciplinary strategy to mind damage in critically sick youngsters and thru the event of finest clinical follow pathways and efficient quality enchancment efforts. As new technology turns into obtainable, the contribution to consequence of poorly characterized physiologic variables, such as autoregulation of cerebral blood circulate, might be better understood. New methods to optimize patient management by way of implementation of evidence-based finest scientific practices will pave the best way for future clinical trials of pharmacological neuroprotective and rehabilitation interventions. Resuscitation of blood strain and oxygenation and prehospital brain-specific therapies for the extreme pediatric traumatic mind harm affected person. Brain accidents and neurological system failure are the most common proximate causes of death in youngsters admitted to a pediatric intensive care unit. Variation in intracranial stress monitoring and outcomes in pediatric traumatic mind injury. Craniocervical arterial dissection in kids: clinical and radiographic presentation and consequence. Pediatric neurocritical care: a neurology consultation model and implication for education and coaching. Emerging subspecialties in neurology: constructing a profession and a area: pediatric neurocritical care. Length of keep and mortality in neurocritically ill sufferers: impression of a specialized neurocritical care staff. Effect of implementation of a paediatric neurocritical care programme on outcomes after extreme traumatic mind damage: a retrospective cohort research. Multimodal monitoring in traumatic mind damage: current standing and future directions. Brain tissue oxygen monitoring after severe traumatic brain harm in kids: relationship to end result and association with other clinical parameters. Transcranial Doppler-based evaluation of cerebral autoregulation in critically unwell children throughout diabetic ketoacidosis treatment. Cerebral hyperemia measured with near infrared spectroscopy during therapy of diabetic ketoacidosis in youngsters. The epidemiology of vasospasm in youngsters with moderate-to-severe traumatic brain harm. Optic nerve sheath diameter as a marker for evaluation and prognostication of intracranial stress in Indian patients: an observational research. Tissue oxygen index: thresholds for cerebral ischemia using near-infrared spectroscopy. Acute care clinical indicators related to discharge outcomes in kids with extreme traumatic mind injury. Incidence of hypo- and hypercarbia in extreme traumatic brain damage earlier than and after 2003 pediatric tips. Cerebrovascular response in infants and young youngsters following extreme traumatic mind harm: a preliminary report. Part 1: relation to age, Glasgow coma score, outcome, intracranial stress, and time after injury. Childhood arterial ischaemic stroke incidence, presenting options, and risk elements: a prospective population-based research. Intelligence after stroke in childhood: evaluate of the literature and ideas for future research. Neurologic end result in survivors of childhood arterial ischemic stroke and sinovenous thrombosis. Report of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke workshop on perinatal and childhood stroke. A multispecialty pediatric neurovascular convention: a mannequin for interdisciplinary management of advanced illness. Use of alteplase in childhood arterial ischaemic stroke: a multicentre, observational, cohort research. Maternal and toddler traits related to perinatal arterial stroke within the infant. Stroke in children: the coexistence of a quantity of danger elements predicts poor outcome. Prospective evaluation of risk elements for recurrent stroke during childhood-a 5-year follow-up examine. Arteriopathy prognosis in childhood arterial ischemic stroke: results of the vascular effects of an infection in pediatric stroke research. Arterial ischemic stroke in neonates, infants and children: an overview of underlying circumstances, imaging methods, and treatment modalities. Risk of recurrent childhood arterial ischemic stroke in a population-based cohort: the significance of cerbrovascular imaging. Ischaemic stroke from dissection of the craniocervical arteries in childhood: report of 12 sufferers. Prognosis of occlusive illness of the circle of Willis (moyamoya disease) in kids. Lipoprotein (a) and genetic polymorphisms of clotting issue V, prothrombin, and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase are risk elements of spontaneous ischemic stroke in childhood. Outcome following decompressive craniectomy for malignant center cerebral artery infarction in kids. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in youngsters: danger elements, presentation, analysis and outcome. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis presenting with extreme subarachnoid hemorrhage in a 14-yearold boy. Management of sickle cell disease: summary of the 2014 evidence-based report by skilled panel members. Therapy insight: stroke risk and its management in patients with sickle cell illness. Pathophysiology and therapy of stroke in sickle-cell illness: current and future. Primary hemorrhagic stroke in kids with sickle cell illness is associated with recent transfusion and use of corticosteroids. Moyamoya syndrome in childhood sickle cell illness: a predictive issue for recurrent cerebrovascular events. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome and silent cerebral infarcts are related to severe acute chest syndrome in children with sickle cell disease. Parent training and biologic factors affect on cognition in sickle cell anemia. Prevention of a first stroke by transfusion in children with sickle cell anemia and irregular results on transcranial Doppler ultrasonography. Discontinuing prophylactic transfusions used to prevent stroke in sickle cell illness. Acute silent cerebral ischemia and infarction during acute anemia in kids with and without sickle cell disease. Controlled trial of transfusions for silent cerebral infarcts in sickle cell anemia. Successful treatment of recurrent basilar artery occlusion with intra-arterial thrombolysis and vertebral artery coiling in a toddler. Are children with acute arterial ischaemic stroke eligible for hyperacute thrombolysis Inadvertent hyponatremia resulting in acute cerebral edema and early evidence of herniation. Use of hypertonic saline within the therapy of extreme refractory posttraumatic intracranial hypertension in pediatric traumatic mind harm. Abnormal regulation of thirst and vasopressin secretion following surgery for craniopharyngioma. Cerebral salt losing syndrome in children with acute central nervous system damage.
Buy slip inn pills in torontoA herbs pictures buy 1pack slip inn overnight delivery, Axial T1-weighted postcontrast picture demonstrates cystic tumor in the best cerebellar hemisphere herbals supplements generic 1pack slip inn visa. C herbs collinsville il cheapest generic slip inn uk, Tilted axial T1-weighted noncontrast picture with superimposed white matter fibers (green) tracked from the superior cerebellar peduncles, demonstrating a medial course with regard to the tumor. D, Oblique sagittal T1-weighted noncontrast image with superimposed superior cerebellar peduncle fibers (green) monitoring superior to the tumor. When it happens, neurological deterioration is usually brought on by worsening obstructive hydrocephalus. Management methods have differed among suppliers, together with preresection shunting, endoscopic third ventriculostomy, or momentary exterior ventriculostomy catheter placement at the time of resection. With few exceptions, the prognosis of newly found cerebellar tumors requires tissue affirmation. Surgery is all the time the first-line remedy because gross whole resection is an important determinant of end result for low-grade gliomas. Of all intracranial low-grade gliomas, cerebellar astrocytomas are probably the most amenable to full resection, which could be healing. In a study of 101 instances of gross totally resected instances, the 10-year progression-free and general survival charges had been 71% and 100 percent, respectively. General anesthesia or sedation could additionally be essential to obtain an sufficient examine in younger youngsters. At surgery, prone positioning of the patient is most well-liked over the sitting place due to the numerous threat of air embolism within the latter. In children younger than 2 years, a horseshoe headrest with padding across the eyes, malar eminences, and brow could additionally be used. If stabilization with the Mayfield-Kees three-point fixation equipment is most well-liked, a padded headrest may be mixed with pins that restrict the utilized stress to 18 pounds or less. Children aged 2 years and older are usually placed in the Mayfield-Kees three-point fixation apparatus; the surgeon applies pin strain utilized slowly while concurrently checking for bone penetration. Capital flexion is critical for reaching lesions that reach to the tentorium or are located close to the top of the vermis. During surgical website preparation, care ought to be taken to include an entry website for a potential posterior ventriculostomy as a end result of this can be essential to decompress the cerebellum if it is extremely tight upon dural opening. For patients older than 2 years, the entry website typically is roughly 7 cm superior and three cm lateral to the inion, although many variations have been described. In younger kids or patients with abnormal head form, intraoperative navigation could be helpful in planning the entry site and trajectory for ventriculostomy. It may also be helpful in figuring out the situation of the torcula or the tumor cyst or in confirming tumor borders adjoining to the cerebellar peduncle or brainstem. Most cerebellar astrocytomas can be safely resected through a midline strategy, although there are some exceptions that will necessitate a extra lateral method. The soft tissues of the neck are dissected along the midline raphe and carried all the way down to the level of the occipital bone and cervical vertebrae. A craniotomy is completed over the midline, from under the inion to the lateral margins of the foramen magnum. The dura is opened in a Y-shaped method and later closed with a triangular dural patch graft. The anesthesiologist should be warned of this possibility at the time of dural opening. It can also be necessary to cannulate and decompress the tumor cyst if cerebellar swelling is severe. Neuronavigation or intraoperative ultrasonography could be helpful for determining the most effective point of entry. A transvermian strategy is commonly used for resection of midline cerebellar tumors. The supracerebellar-infratentorial approach can be used for high vermian lesions. Care is required when the veins between the cerebellum and the undersurface of the tentorium are sacrificed as a end result of they can be a source of significant bleeding. If the tumor has an related cyst, this could be entered early to find a way to decompress the encompassing cerebellum. A circumferential airplane is developed surrounding the lesion with the use of light retraction and bipolar electrocautery. Lesions with brainstem or cerebellar peduncle involvement necessitate caution at the lateral and ventral margins to keep away from damage to these constructions, even if it means leaving a small quantity of residual tumor. The dura is closed with the use of autologous pericranium in an older child or a dural substitute for added reinforcement. The muscle and fascia are then reapproximated with absorbable suture, and the skin is closed in the standard method. If a ventriculostomy catheter was positioned, the patient is generally weaned from it or transitioned to a shunt over the course of the instant postoperative week once the neurological examination yields steady, reliable findings. If feasible, repeat surgical procedure could also be thought of on the time of recurrence; after a second subtotal resection, roughly 70% of cases present spontaneous regression. Initial chemotherapeutic regimens mostly in use embrace both a mixture of carboplatin and vincristine or a combination of 6-thioguanine, procarbazine, lomustine, and vincristine. The use of radiation within the treatment of cerebellar astrocytomas is generally restricted to older children with recurrent or refractory tumors in whom chemotherapy has had no profit. The signs of cerebellar mutism may be secondary to damage to the dentatothalamocortical pathway. Efferent alerts from the dentate nuclei travel via the superior cerebellar peduncle and, to a lesser extent, the middle cerebellar peduncle. They then cross to the contralateral ventrolateral thalamus and finally to the first and premotor cortices. In addition, the 2 dentate nuclei have connectivity via the Guillain-Mollaret triangle and the inferior olivary nucleus. These connections are key in regard to initiation of movement and cortical processing. The prognosis for a patient stricken with speech deficits 1 yr postoperatively is reported as 32% deficit decision. Aseptic meningitis develops approximately 5 to 7 days after surgery and can coincide with the onset of steroid tapering. After the initiation of remedy, affected kids sometimes do nicely with out long-term dysfunction. This could manifest as an incidental finding on postoperative imaging or, in rare circumstances, as a big, fluctuant mass underlying the surgical incision. Age at preliminary diagnosis was a optimistic predictive factor for the event of these deficits. At long-term follow-up, affected children were discovered to lead a more sedentary lifestyle because of their physical limitations. Patients with a greater premorbid socioeconomic status report better high quality of life postoperatively. In the small percentage of sufferers with recurrent disease, more frequent imaging and mixed chemotherapy, radiation remedy, and re-resection could also be required. Neurosurgeons also needs to pay consideration to the necessity for ongoing improvement measures for long-term quality of life. In fact, some authors argue that aggressive radiographic evaluation is most likely not useful as a end result of it has a low medical yield. Patients are then monitored yearly until progression-free survival has reached 5 years after which each other yr for an additional 5 years. Surgical and medical elements of cerebellar pilomyxoid�spectrum astrocytomas in youngsters. Long-term outcome after resection of benign cerebellar astrocytomas in youngsters and young adults (0-19 years): report of one hundred ten consecutive cases. A population-based research of the incidence and survival charges in sufferers with pilocytic astrocytoma. Spontaneous cerebellar hemorrhage due to a juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma: case report and review of the literature. Apparent diffusion coefficient of pediatric cerebellar tumors: a biomarker of tumor grade Management of recurrent pilocytic astrocytoma with leptomeningeal dissemination in childhood. Aseptic meningitis after posterior fossa surgical procedure treated by pseudomeningocele closure. Placement of occipital condyle screws for occipitocervical fixation in a pediatric affected person with occipitocervical instability after decompression for Chiari malformation.
|

