Cafergot
"Generic 100 mg cafergot overnight delivery, diagnostic pain treatment center tomball texas". C. Ayitos, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D. Clinical Director, VCU School of Medicine, Medical College of Virginia Health Sciences Division

Chapter 184: Revision Rhinoplasty 3043 Case Presentation Five-Revision of the Severely Collapsed Nose Brief Oase History A wholesome younger feminine presents 18 months after severe nasal trauma complaining of severe nasal obstruction and a large, flat, and crooked nasal vault Four weeka prior to injwy, the patient underwent reduction rhinoplasty for treatment of a large nostril with severe airway obstruction. Postopera~ photographs reveal overresection of the ihinion, deprojection of the nasal tip, and important additional widening of the tip and doiSum (see F"xg. Upon presentation 18 months after harm, frontal examination revealed a splayed and scoliotic nose with impaction of the bony vault. On profile examination, conspicuous loss of doiSal, tip, and columellar projection had been evident, whereas the basal view revealed a severely underprojected nostril with widening and impaction of the caudal septum. A 5-cm section of full-thickness cartilage was harvested from the best fifth rib through an inframammary fold incision. The septal alternative graft was sutured to the higher lateral cartilages on the K-area and to the columellar strut to reconstitute the L-sttut. A 4 x 5 em piece of deep temporalis fascia is harvested from the right temporal scalp. Upon degloving of the center vault, the dorsal septum was found avulsed from the nasal bones, partially collapsed into the nasal cavity, and canted approximately 30 degrees to the right of midline. The caudal septum was deviated roughly 90 levels from sagittal and was protruding into the best nasal passage. The alar cartilage remnants are deglaved, and the contractured vestibular pores and skin is unfurled with lysis of scar adhesions. The nasal pores and skin is closed Wlder average rigidity and measured tip projection increased by 12 mm. Smooth and attractive dorsal strains are achieved with diced cartilage wrapped in temporalis fascia. In addition to the technical challenges associated with profound cosmetic derangements, surgically compromised tissues and the emotional impact of an sudden nasal deformity add to the already formidable remedy challenge. Familiarity with each graft type and its distinctive biophysical properties is essential to profitable graft application, and a creative sensibility to information surgical intervention is invaluable. For most sufferers, the goal of an attractive, durable, and totally functional nostril could be achieved when these methods are executed efficiently; and the emotional impact of a successful revision rhinoplasty can be each dramatic and immensely gratifying for affected person and surgeon alike. Anatomic basis and medical implications for nasal tip help in open versus closed rhinoplasty. Awareness and identification of physique dyamorphic disorder by aesthetic surgeons: outcomes of a survey of American society for aesthetic plastic surgery members. Objective evaluation of the accuracy of computer-simulated imaging in rhinoplasty. Comparison of ondansetron and combination of ondansetron and dexamethasone as a prophylaxis for postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults present process elective laparoscopic surgical procedure. The impact of mixing dexamethasone with ondansetron for nausea and vomiting assodated with fentanyl-based intravenous patient-controlled analgesia. Use of porous high-density polyethylene (medpor) forspreader or prolonged septal graft in rhinoplasty: � An in-depth review of skeletal overresection-perhaps the most typical drawback prompting advanced revision rhinoplasty-including the cosmetic. Chapter 184: Revision Rhinoplasty aesthetics, useful outcomes, and long-term issues. Revision rhinoplasty utilizing porous high~ensity polyethylene implants to reestablish ethnic identity. Use of porous high-density polyethylene in ~sion rhinoplasty and the platyrrhine nostril. Straightening the crooked middle third of the nose: using porous polyethylene prolonged spreader grafts. Long-term use and follow-up of irradiated homologous costal cartilage in the nostril. Osseocartilaginous rib graft rhinoplasty: a stable predictable method for major dorsal reconstruction. Human nasal cartilage ultrastructure: traits and comparison using scanning electron microscopy. An anatomic and histologic evaluation of the alar-facial crease and the lateral crus. Observations of the marginal incision and lateral crura alar cartilage asymmetry in rhinoplasty: a hard and fast cadaver study. Anatomical characterisitics of the conchal cartilage with advised clinical functions in rhinoplasty surgical procedure. Internal stabilization of autogenous rib cartilage grafts in rhinoplasty: a barrier to cartilage warping. Diced cartilage grafts in rhinoplasty surgery: present techniques and functions. Nasal tip blood provide: an anatomic study validating the sakty of the transcolumellar incision in rhinoplasty. Septal extension grafts ~sited: 6-year expertise in controlling nasal tip projection and form. Nose elongation: a ~ew and outline of the septal extension tongue-in-groove approach. The alar contour graft: correction and prevention of alar rim deformities in rhinoplasty. Viability of crushed human auricular and costal cartilage chondrocytes in cell tradition. The extracorporal septum plasty: a way to right troublesome nasal deformities. Reconstruction of the nasal septum utilizing perforated and unperforated polydioxanone foil. Adamson Addressing the higher third of the face is a crucial part of facial rejuvenation. For many sufferers, descent of the eyebrows results in exacerbation of periorular getting older, which is inadequately treated with blepharoplasty. Without correction of eyebrow ptosis, the growing older face usually conveys fatigue and even anger. Forehead rejuvenation procedures have been utilized with growing frequency during the last a quantity of a long time. Some of the earliest descriptions of forehead lifting date back to 1919 as described by Passot, Hunt, and Lexer (2). Vinas is credited for noting the difference between static and dynamic rhytids and importantly recognized that therapy would differ between the two types, together with the necessity to free adhesions over the orbital rims to mobilize and elevate the brows. An important development in forehead lifting occurred in 1992 with the first description of the endoscopic technique (3). Despite a quantity of modifications of the forehead raise trending toward much less invasive approaches purporting decrease complication rates and better affected person acceptability. The decrease anatomic boundaries embody the supraorbital rim, nasal root, and bony zygomatic arches. Perhaps an important division of brow anatomy lies on either facet of the temporal line, which divides the temporal areas from the forehead and intersects with the peak of the brow in both men and women. Branches of the external and inside carotid arteries provide the blood supply to the brow. The external carotid artery supplies the superficial temporal artety and subsequent zygomaticotemporal department, which supply the temple region and lateral brow. The internal carotid artety supplies the midforehead via branches of the ophthalmic artery, the supratrochlear artery medially, and the supraorbital artery laterally, usually 2. Sensation is provided by the supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves, that are branches of the trigeminal nerve (V). The supraorbital nerve exits the superior orbit by way of a foramen alongside the rim in practically 90% of patients but can even exit the orbit via a foramen as a lot as 1. Laterally, sensation is offered by the lacrimal (V1), zygomaticofacial (V2), and aurirulotemporal (V3) nerves. Motor innervation is supplied exclusively by the notoriously fragile temporal department of the facial nerve. The temporal department exits the parotid gland and courses superiorly from a degree 1. This nerve can be reliably predicted by its relation to what 3053 3054 Section X: Facial Plastic and Reconstn. The temporal department remains simply deep to the temporoparietal fascia and rum inside the substance of this fascia. The forehead is an atension of the scalp and thus consists of the same layers, which.
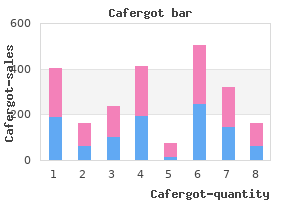
There is usually fibrous connective tissue present instead of the native cartilaginous junction. Therefore, preservation of the mucoperichondrium and creation of a pocket for graft placement by way of the open method are normally most popular. If the higher lateral cartilages are fused with the septum within the inner nasal valve space. In instances in which the upper lateral cartilages have been virtually completely resected, conchal cartilage onlay grafts may be wanted in addition to spreader grafts to increase lateral assist or camouflage depressions. In basic, the grafts ought to run alongside the dorsal septum from below the bony cartilaginous junction to the anterior septal angle. Grafts of unequal width may also be used to correct asymmetries within the middle vault. Spreader grafts may additionally be used as internal splints to help straighten a caudal septal deflection. Placement of spreader grafts is significantly facilitated by placement of a 30-gauge needle by way of the cartilage advanced while suturing. A corollary to spreader grafting that deserves point out is reverse spreader grafting. In these instances, sufferers can benefit from discount of the horizontal width of the cartilaginous dorsum, which may be thought of as the reverse of spreader grafts (23). Additional methods to increase the operate of the nasal valve involve the position of alar batten grafts, butterfly grafts, and varied suture strategies. Schlosser and Park (24) described the use of 5-0 pricey nylon flaring sutures that span the upper lateral cartilages and septum horizontally. Tightening the suture theoretically will increase the angle of the interior nasal valve and due to this fact improves nasal airflow. Their research indicated that flaring sutures used concomitantly with spreader grafts increase airflow more than the use of spreader grafts alone. Other suture strategies corresponding to tip-lifting sutures, or valve maneuvers like inside valve M-plasty or lateral crural J-flap, may additionally be useful adjuncts but are outdoors the scope of this chapter. Patients with saddle-nose deformity frequently have middle vault collapse without gentle tissue help. Fixation of a dorsal graft helps to enhance dorsal projection, assist the delicate tissues, and restore the integrity of the nasal valve. Calvarial bone secured with a lag screw or rib cartilage 2958 Section X: Facial Plastic and Reconstn. In addition, dorsal calvarial grafts can serve as anchors for different reconstructive grafts (27). It is brought on by relative undetprojection of the nasal tip with regard to the projection of the dorsum. It is important to understand that a pollybeak can ocarr, subsequently, when the tip is both corTectly projected or tmdetprojeaed. If tip projection is aesthetically right however the dorsum stays overprojected, a pollybeak defonnity is present Conversely, a pollybeak outcomes when dcmal projection is aesthetically appropriate however the tip is undetprojected. As such, there are different administration stmtegies for minimizing the incidence of pollybeak, relying on the character of the deformity. The essential point is that the Ihinoplasty swgeon acknowledges the importance of the important relation between tip projection and dorsal projection throughout rhinoplasty and maintains adequate tip projection when altering the dorsum. Chapter 181: the Nasal Dorsum: Management of the Upper Two-Thirds of the Nose 2959 Profile of nose earlier than hump elimination A~fil~~~. Techniques used to accomplish these aims embody hump reduction, osteotomies, and grafting. Improper or incomplete therapy of the bony vault could result in suboptimal results, including persistence of present defectB or the creation of latest ones. Regional dorsal ove:rprojection is managed with wide gentle tissue envelope elevation and the removing of parts of the nasal bones. Early techniqua had been fraught with nasal airway compromise largely because of a trajectory that caused broad disruption of periosteum and launch of decrease lateral cartilage lateral suspensory ligaments. Modifications have led to the eme:rgence of modem methods that place equal significance on preservation of the nasal airway and aesthetic improvement in accord with the dual tenet of the rhinoplasty operation (32,33). Osteotomies are generally used to enhance irregularities in the brow- tip aesthetic line and correct open roof deformities (diastasis of the nasal bones) related to bony dorsum discount. Lateral osteotomies must be limited to the skinny bone of the pyriform aperture, lateral to the anterior maigin of the ascending maxiihuy processes. The auved, guarded 4-mm osteotome is placed into the inc:iaion on the margin of the pyriform aperture, at a couple of 45-degree angle to the facial airplane. Preaervation of the inferior Begment of the pyriform maintains the lateral suspensory ligaments and width necessary for the nasal airway. The osteotomy ought to then curve anteriorly and superiorly to terminate on the 1~ of the medial canthus, midway between the donal line and the medial canthus. The telltale sound of the osteotome meeting the thiclc�r frontal bone is indicative of the right stopping level. Elevation of the periosteum on this vicinity liberates the nasal bones from the delicate tissue envelope. Bone removing iJ subaequmdy achieved with a double-guarded osteotome or a carbide ~ten pull rasp, relying on the quantity of bone to be removed. Refinemmta can then be pexfurmed by rasping just off midline in a slightly oblique method so as not to avulse the upper lateral cartilages (30). It should always be remembered that overly aggressi~ bony and cartilaginous dorsal reduction can lead to a scooped nasal look and even the saddle-no$e deformity. The osteotomy is then tran� sitioned (position 2) and carried to Ute medial c:an1hal area. Perforating lateral osteotomies could be carried out either internally (transnasally) or akmally (percutaneously). The perforating approach is the best technique to complete a precise osteotomy with minimal trauma. A series of perforations are made at mounted intemlls alongside the specified fracture trajectory after which completed with minimal handbook manipulation. The intranasal perforating osteotomy is beneficial to widen the pyriform aperture by displacing the bones laterally (37). Medial and intennediate osteotomies must be used judiciously; howevet they can be essential when the pyriform is vecy thick, the nostril is considerably deviated, or a vecy massive nostril needs to be reduced. Both medial and intermediate osteotomies are normally performed transnasally with a 3-mm osteotome. Medial a~teotomies are initiated on the medial side of the caudal margin of the nasal bones close to the septum. The percutaneous perforation approach can be used to perform medial osteotomies to further ensure preservation of the keystone. The intennediate a~te otom:y can also be initiated on the caudal margin of the nasal bones, intermediate to the medial and lateral osteotomies. Because intermediate osteotomies are tough to execute if the lateral bone has already been mobilized. It is usually helpful to plan the steps wanted to reshape the higher two-thirds of the nostril. Drawing the strains of deliberate osteotomies and indicating these areas to be grafted or decreased will help information the operation in a logical method. The graft is placed either superficial or deep to the nasal bone periosteum and held in place by the overlying pores and skin envelope. These grafts are cantilevered off the frontal bone and anchored precisely with titanium screws. Spreader graft: a way of reconstructing the roof of the middle nasal vault following rbinopla. Deformities affecting the nasal vaults are distinct and unbiased from those affecting the nasal tip and contribute not solely to umightly look but in addition to improper nasal function. Building on the past expertise of prior rhinoplasty swgeons, surgical methods dealing with nasal vault deformities have evolved, ever aware that restoration of proper anatomic vault relations significantly enhances the looks of the nostril and nasal perform. The up to date rhinoplasty surgeon have to be facile with analysis and administration of the bony and cartilaginous nasal vaults that comprise the higher twothirds of the nose and be succesful of integrate this into management of the nasal tip for successful efficiency of the rhinoplasty operation.
One must control precisely the depth of the abrasion grew to become prominent sc:a:rring occun if abrasion penetrates reticular dermis. Thermal injury to surrounding tissues could be additional decreased by pulsing the laser emission (selective photothermolysis). Hemostatic Agents Hemostatic brokers are used to management bleeding from removal of superficial cutaneous lesions, which often results in capillary or venous bleeding. Monsel solution (ferric subsulfate) is a protein coagulant that may be very efficient however carries the slight risk of permanent discoloration from iron pigment deposition. Silver nitrate comes conveniently in a stick kind or answer however is less effective than Monsel answer or aluminum chloride and can stain skin. Dermatosis papulosa nigra is handled with light electrodesiccation using fine-tipped cautery needles, then curettage. Multiple lesions could require several periods or alternative therapies, together with dermabrasion, chemical peeling, topical 5-fluorouracil (Efudex, Fluoroplex), or topical imiquimod. Healing occurs over 6 to eight weeks and is accelerated by means of topical corticosteroids. Results are glorious however not permanent, with retreatment usually needed in 2 to 3 yeatS. Imiquimod 5% cream was accredited in 2004 for the remedy of actinic keratosis of the face or scalp. Whether administered as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy, topical therapies provide the opportunity to successfully handle actinic keratosis and will doubtless emerge as an essential software for health care suppliers (24). Lasers emit coherent gentle at particular wavelengths peculiar to the lasing material. This mild power is selectively absorbed by particular pores and skin structures (chromophores) and transformed into Cutaneous Horns Cutaneous horns are completely removed (shave or punch technique) so the base can be examined histologically. If a squamous cell or basal cell carcinoma is confinned by histologic examination, a wider excision is carried out. Epidermal Cysts Small infected cysts occur with acne vulgaris and are handled with intralesional steroids in concentrations of two to 5 mgf mL. This ends in full resolution in three to 5 days, with a low incidence of recurrence. The injection could trigger temporary dermal atrophy, which resolves in 6 to 12 months. Infected cysts are typically giant and of longer duration than small acne-associated cysts. These are finest handled with systemic antibiotics, particularly these with further antiinflammatory results such as tetracycline and erythromycin. For tense and severely infected lesions, incision, drainage, culture, and sensitivity willpower ought to be performed, and the treated lesions must be full of iodoform gauze. Surgical remedy is deferred for 4 to 6 weeks after infection as a end result of infection thins the cyst wall and dermal collagen, making the process difficult and growing the probabilities of infection spreading. The remedy of noninfected, noninflamed cysts is surgical, with full cyst wall removing (to forestall recurrence). Freely cellular cysts have little reference to the overlying epidermis and are easily removed. Injection of local anesthetics between the cyst wall and surrounding tissues (hydrodissection) facilitates surgical removal. If the cyst is firmly adherent to the encompassing tissues, the complete cyst and surrounding fibrous tissue are excised. The use of a punch biopsy as an alternative of an ellipse may present a gap massive sufficient to take away the cyst with wonderful beauty results. Epidermal cysts that are freely or partially cell may be eliminated by way of incisions at distant sites the place cosmetic elements are overriding. If the cyst wall ruptures with spillage of keratinous materials, the world is irrigated with regular saline and all recognizable 3226 Section X: Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery keratinous debris is removed. Necrosis of overlying pores and skin as soon as a cyst is eliminated normally occurs when a large cyst has been removed, resulting in massive lifeless area with overlying dermis. To avoid necrosis, all underlying useless space is removed and tension on the pores and skin edges is minimized. Dermabrasion and C02 laser permit the surgeon to sculpt with management and precision, the latter sustaining a relatively bloodless subject. Removing tissue below the pilosebaceous apparatus ends in an unattractive, unnaturally smooth, poreless scar. Milia A milia is treated by incising its roof and extracting its keratinous core with a milia comedo extractor. Smaller dosed comedones and open comedones (blackheads) are treated with topical retinoic acid (Retin-A). Hidrocystoma the hidrocystoma cyst is surgically excised if necessary for beauty reasons. Syringoma Syringomas usually present as a number of lesions; therefore, surgical excision is often not feasible. Dermabrasion and superficial C02 laser offer honest outcomes on those chosen lesions which are more cosmetically concerning to the affected person. Trichofolliculomas Trichofolliculomas are eliminated by shaving, punch excision with suturing, or vaporization with a C0 2 laser. Trichoepitheliomas Solitary trichoepitheliomas are removed the same way as trichofolliculomas. However, distinction of basal cell cardnoma and solitary trichoepithelioma is difficult each clinically and pathologically. Multiple trichoepitheliomas are removed with dermabrasion and C02 laser with glorious outcomes. Hemangiomas Most capillary hemangiomas resolve spontaneously, so remedy is normally not essential. Exceptions are hemangiomas that ulcerate, encroach on a significant construction (nose, eyes, mouth), or are incessantly traumatized (buttock. For these, medical remedy (prednisone and interferon alfa) or intralesional corticosteroids are used. A nevus flammeus (port-wine stain) is treated with tunable dye lasers or, extra lately, copper vapor, krypton, or flashlamppumped pulsed-dye lasers (Table 195. Complications are unusual with these methods, with occasional hypopigmentation or pores and skin texture alterations. Lesions in dark-skinned patients lighten less than others because epidermal melanin causes some absorption of the laser gentle. Pilomatricomas Pilomatricomas, deep-seated nodules, require surgical excision in most cases. Trichilemmomas Solitary lesions of trichilemmoma are handled as trichofolliculomas. Pyogenic Granuloma Nevus Sebaceus A nevus sebaceus lesion is usually completely excised because it has malignant potential; nevertheless, its risk for malignancy is low. It also could additionally be adopted for changes of malignancy and handled at a later date if needed. Pyogenic granulomas are treated aggressively because recurrence is widespread if excision is incomplete. Shave elimination with electrosurgery of the base is easy and effective, as is elliptical excision. Ablation with a C02 laser, argon laser, dye laser, or copper vapor laser is also effective. Telangiectasias Sebaceous Hyperplasia Sebaceous hyperplasia lesions are handled with cryotherapy or gentle electrodesiccation with fine-tipped cautery needles. Telangiectasias could be treated merely with electrodesiccation using fine cautery needles (epilating needles). Telangiectasias also could be treated with laser therapy (argon, argon-pumped tunable dye. Excessive sebaceous tissue is excised Chapter 195: Management of Benign Facial Lesions 3227 some sclerosant into the cavernous sinus or deep venous drainage of the head and neck, inflicting probably grave issues.
|